The Role of Microgrids in Modern Energy Systems
By Bascon | Posted Sep 09, 2023
In the rapidly evolving landscape of energy distribution, microgrids have emerged as a transformative solution with the potential to revolutionize the way we generate, distribute, and consume electricity. These small, self-contained energy systems are changing the game for communities, businesses, and even entire regions. In this article, we explore the concept of microgrids, their advantages, and their promising future in the energy sector.
What Are Microgrids?
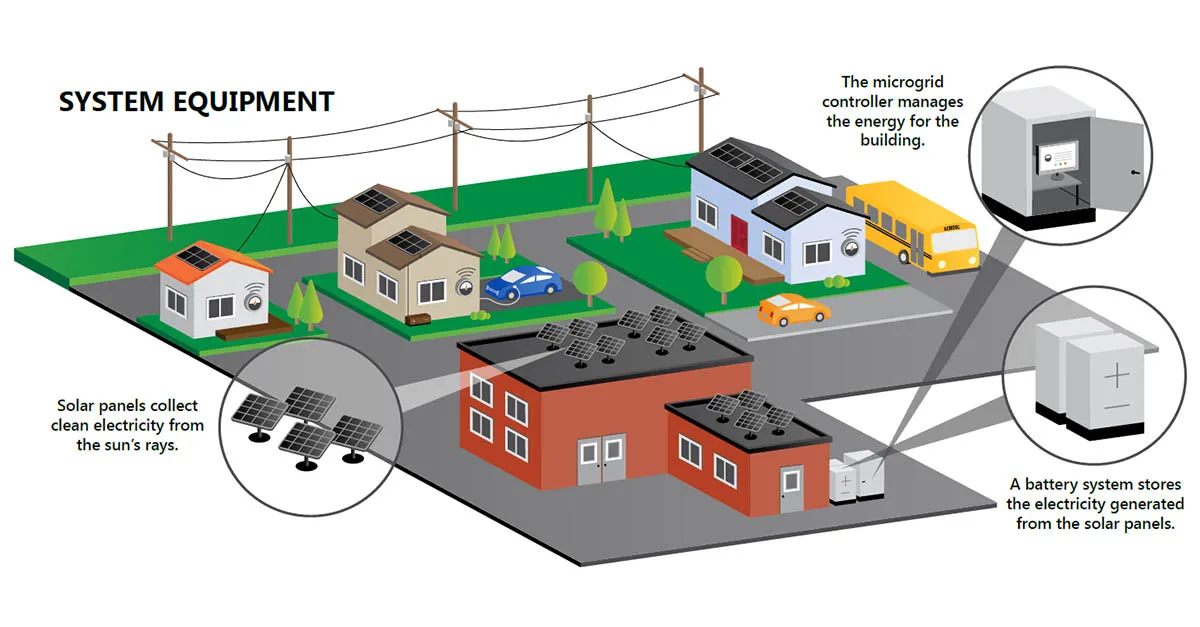
A microgrid is a localized, independent energy system that can operate autonomously or in conjunction with the main power grid. Comprising a mix of power sources, including renewable energy (such as solar panels and wind turbines), battery storage, and traditional generators, microgrids are designed to provide reliable electricity to a defined area, often a community, campus, or industrial complex. They can be grid-connected or isolated, offering flexibility and resilience in the face of disruptions.
Advantages of Microgrids
- Resilience and Reliability: Microgrids are designed to operate independently, reducing vulnerability to power outages caused by grid failures, extreme weather events, or other emergencies. This resilience is particularly vital for critical infrastructure, such as hospitals, military bases, and data centers.
- Energy Independence: Communities and organizations with microgrids can reduce their reliance on centralized power generation. By integrating renewable energy sources, they can generate cleaner, more sustainable electricity locally, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to environmental goals.
- Cost Savings: Microgrids can help lower electricity costs over time. By generating electricity on-site and optimizing energy usage, they can reduce dependence on expensive grid electricity, especially during peak demand periods.
- Efficiency: Microgrids can be highly efficient due to their ability to capture waste heat and use it for heating or cooling, increasing overall energy utilization and reducing energy waste.
- Scalability: Microgrids are adaptable to different scales, from small residential communities to large industrial complexes. They can be expanded or contracted based on the needs of the user, making them a versatile solution.
- Grid Support: Microgrids can also provide grid support by offering services like frequency regulation and demand response. They can stabilize the grid during fluctuations and support its overall reliability.
Use Cases
- Remote Communities: In remote or off-grid areas, microgrids can provide a lifeline for electricity access. They enable communities to have a stable power source, improving living conditions, and enabling economic development.
- Industrial and Commercial Facilities: Many industries and businesses are turning to microgrids to enhance their energy resilience, reduce operating costs, and meet sustainability goals.
- Military and Defense: Microgrids are increasingly used on military bases to ensure continuous power supply for mission-critical operations.
- Emergency Response: Microgrids can be quickly deployed to provide emergency power during natural disasters, helping to restore critical services and infrastructure.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While microgrids offer numerous benefits, they are not without challenges. These include initial setup costs, regulatory hurdles, and interoperability with the existing grid. However, as technology advances and policies evolve, these barriers are gradually being overcome.
The future of microgrids is promising. As they become more affordable and scalable, we can expect to see wider adoption across various sectors. Microgrids will play a pivotal role in transitioning to a cleaner, more resilient energy landscape, enhancing energy access, and supporting sustainability goals. In an increasingly decentralized energy world, microgrids empower communities and organizations to take control of their energy future, one grid at a time.
Recent Industry Insights
-
 How Solar and Batteries Are Transforming the Corporate Landscape
How Solar and Batteries Are Transforming the Corporate LandscapeHow Solar and Batteries Are Transforming the Corporate Landscape
-
 The Role of Microgrids in Modern Energy Systems
The Role of Microgrids in Modern Energy SystemsThe Role of Microgrids in Modern Energy Systems
-
 How Solar Energy Benefits Australian Homes
How Solar Energy Benefits Australian HomesHow Solar Energy Benefits Australian Homes
-
 The Electrifying Rise of Electric Vehicles in Australia
The Electrifying Rise of Electric Vehicles in AustraliaThe Electrifying Rise of Electric Vehicles in Australia
